Dekan Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), Prof. Muhammad Kamal, S.Si., M.GIS., Ph.D., menegaskan pentingnya integritas, moralitas, dan tanggung janji bagi pejabat baru di lingkungan Fakultas Geografi UGM sebagai tiga poin utama dalam menjalankan tugas manajerial. Penegasan tersebut disampaikan dalam acara Serah Terima Jabatan Ketua Departemen dan Ketua Program Studi periode 2026–2031 serta Kepala Laboratorium Tata Ruang Wilayah yang digelar pada Rabu (07/01/26) di Ruang Sidang A201 Fakultas Geografi UGM.
Mahasiswa Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) yang tergabung dalam Himpunan Mahasiswa Geografi Pembangunan (HMGP) melaksanakan kegiatan pengabdian kepada masyarakat melalui program HMGP Mengabdi pada 22–23 November 2025 di Desa Wisata Srikeminut, Dusun Wunut, Kalurahan Sriharjo, Kapanewon Imogiri, Kabupaten Bantul.
Kegiatan ini merupakan salah satu bentuk implementasi Tri Dharma Perguruan Tinggi, khususnya pengabdian kepada masyarakat. Pada tahun ini, program HMGP Mengabdi difokuskan pada edukasi kesehatan, penguatan ketahanan desa, peningkatan kapasitas masyarakat, serta pembangunan relasi berkelanjutan antara mahasiswa dan warga.
Bencana banjir yang melanda sejumlah wilayah di Sumatra beberapa waktu lalu turut berdampak pada mahasiswa Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM). Merespons kondisi tersebut, Fakultas Geografi UGM menyalurkan bantuan kemanusiaan kepada 10 mahasiswa dari program sarjana dan pascasarjana yang berasal dari wilayah terdampak.
Bantuan yang diberikan tersebut berupa bantuan biaya hidup serta pembebasan Uang Kuliah Tunggal (UKT) untuk semester genap Tahun Akademik 2025/2026. Penyerahan bantuan dilakukan secara simbolis kepada empat perwakilan mahasiswa terdampak pada Rabu (24/12) di Ruang A201 Fakultas Geografi UGM.
Dalam rangka mendukung pengembangan pariwisata berkelanjutan dan pemberdayaan masyarakat, Tim Laboratorium Tata Ruang Wilayah melaksanakan kegiatan pengabdian kepada masyarakat untuk mengkaji perkembangan pariwisata di Desa Wisata Srikeminut.
Kajian mengenai pengembangan desa wisata tersebut dipilih sebagai respon tindak lanjut dari peningkatan tren pembentukan desa wisata yang mengangkat nilai keunikan budaya lokal. Desa Wisata Srikeminut sendiri memiliki potensi wisata alam, wisata budaya, dan wisata buatan berbasis edukasi yang dapat terus dikembangkan sebagai modal sosial-ekonomi masyarakat.
Workshop yang berlangsung pada 1–5 Desember 2025 di CIFOR-ICRAF Campus, Bogor, mempertemukan para akademisi, praktisi, dan mahasiswa yang didukung oleh International Model Forest Network (IMFN) di Asia, proyek ERASMUS+ FORSU, serta sejumlah mitra undangan lainnya.
Pada kegiatan ini, tim berkolaborasi mengembangkan kurikulum restorasi lanskap yang merupakan keberlanjutan dari workshop pada April 2025 lalu. Dua diantaranya merupakan dosen sekaligus tenaga ahli dari Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), yakni Dr. Dyah Rahmawati Hizbaron dan Utia Suarma. Keduanya terlibat aktif dalam penyusunan modul Socio-Ecological Systems and Landscape Approach serta modul Governance and Policy Planning for Landscape Restoration.
Upaya Indonesia mencapai FOLU Net Sink 2030 memasuki tahap penting dengan diluncurkannya mekanisme penilaian dan geoportal praktik baik Ecosystem-based Approach (EbA) oleh Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM). Wakil Rektor Bidang Penelitian, Pengembangan Usaha, dan Kerja Sama UGM, Danang Sri Hadmoko, menegaskan bahwa inovasi ini menjadi tonggak percepatan kontribusi Indonesia dalam penurunan emisi.
“Geoportal dan mekanisme penilaian EbA ini adalah langkah konkret kami untuk menghadirkan data yang terbuka, terstandar, dan dapat langsung dimanfaatkan oleh pengambil kebijakan,” ujarnya (9/12) dalam pembukaan Diseminasi Hasil Pemetaan EbA pada 9–10 Desember 2025 di Grand Keisha Hotel Yogyakarta.
Dosen Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), Prof. Dr. Rini Rachmawati, S.Si., M.T., berpartisipasi dalam German–Southeast Asian ForUm of Urban Experts’ Conference yang diselenggarakan pada 24–30 November 2025 di Köln, Jerman. Konferensi ini diselenggarakan oleh Institute of Geography, University of Cologne dengan dukungan dari DAAD.
Dalam forum tersebut, Prof. Rini menyampaikan paparan tentang Integrating Smart Sustainable City Frameworks into Disaster Risk Reduction and Preparedness Strategies in Jakarta and Nusantara, Indonesia. Konferensi ini sekaligus memperingati hari jadi ke 20 tahun ForUm, yang telah aktif menyelenggarakan kegiatan pertukaran akademik dan diskusi keilmuan sejak 2005.
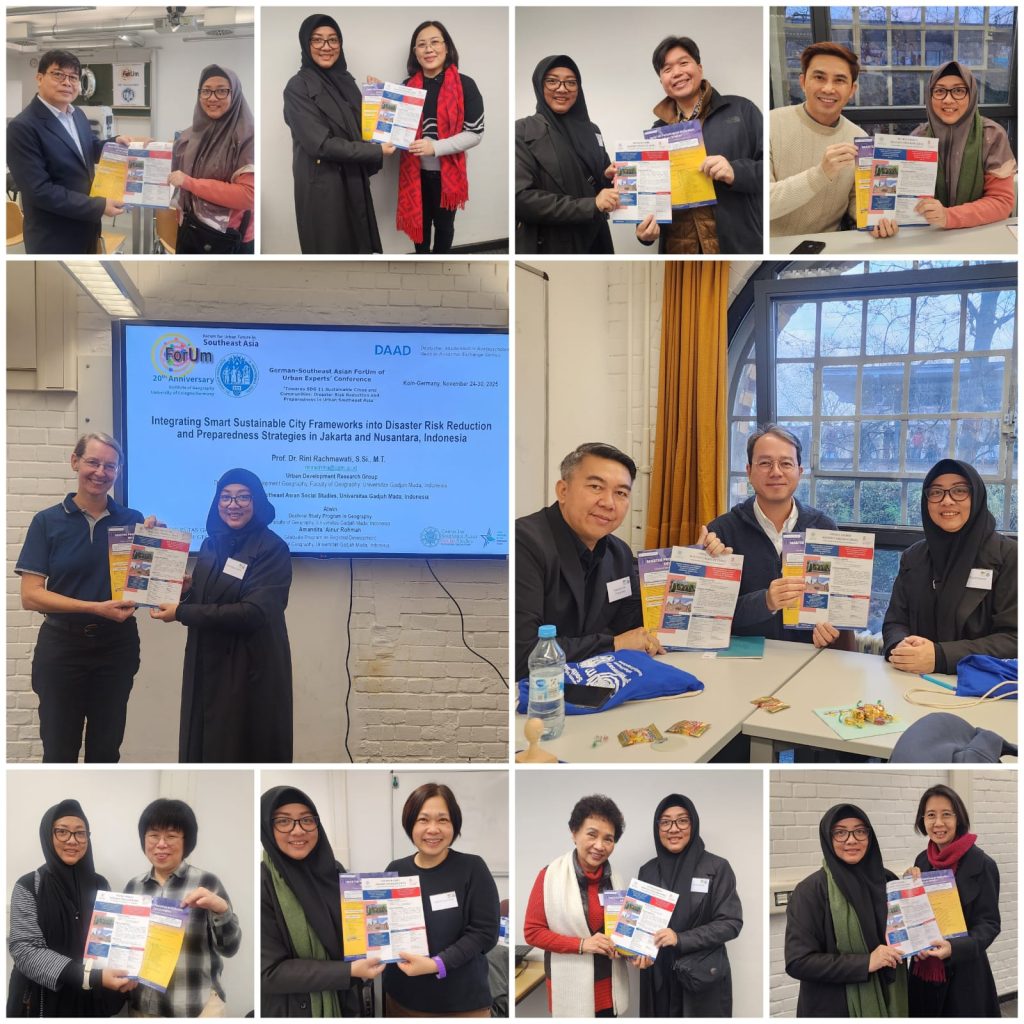 Prof. Rini yang juga menjabat sebagai Ketua Minat Studi Pembangunan Wilayah (MPW) Fakultas Geografi UGM, turut memanfaatkan kesempatan tersebut untuk memperkenalkan program akademik unggulan UGM. Ia menyampaikan informasi serta membagikan leaflet Double Degree Program on Sustainable Urban and Regional Development (SURD–MPW) UGM-University of Groningen dan Regular Program of Regional Development (Minat Studi Pembangunan Wilayah/MPW) kepada para kolega akademisi dari kawasan Asia Tenggara dan Jerman, khususnya yang berasal dari berbagai perguruan tinggi di Jerman, Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, Filipina, Myanmar, Malaysia, dan sejumlah negara lainnya.
Prof. Rini yang juga menjabat sebagai Ketua Minat Studi Pembangunan Wilayah (MPW) Fakultas Geografi UGM, turut memanfaatkan kesempatan tersebut untuk memperkenalkan program akademik unggulan UGM. Ia menyampaikan informasi serta membagikan leaflet Double Degree Program on Sustainable Urban and Regional Development (SURD–MPW) UGM-University of Groningen dan Regular Program of Regional Development (Minat Studi Pembangunan Wilayah/MPW) kepada para kolega akademisi dari kawasan Asia Tenggara dan Jerman, khususnya yang berasal dari berbagai perguruan tinggi di Jerman, Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, Filipina, Myanmar, Malaysia, dan sejumlah negara lainnya.
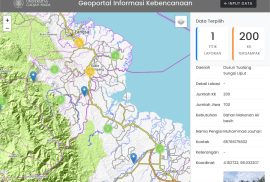
Bencana banjir dan longsor melanda sejumlah wilayah di Sumatera sejak 25 November hingga awal Desember 2025. Dalam kondisi darurat tersebut, distribusi bantuan kerap menghadapi kendala, mulai dari ketidakmerataan hingga ketidaksesuaian dengan kebutuhan di lapangan akibat minimnya informasi detail. Akibatnya, bantuan menumpuk di satu lokasi sementara wilayah lain justru mengalami kekurangan.
Merespons situasi tersebut, Tim Quick Mapping Bencana Sumatera Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) menginisiasi Geoportal Informasi Kebencanaan (GIK) sebagai upaya darurat untuk memastikan penyaluran bantuan berlangsung lebih merata dan tepat sasaran. Geoportal ini diluncurkan dan disebarluaskan kepada publik pada Minggu (7/12).
Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) menggelar konsolidasi antar unit kerja sebagai upaya memperkuat komitmen kampus berkelanjutan dalam pelaksanaan Tri Dharma Perguruan Tinggi dan tata kelola green campus. Kegiatan tersebut berlangsung pada Rabu (3/12) di Ruang Sidang A201 Fakultas Geografi UGM.
Konsolidasi ini merupakan bagian dari rangkaian program UGM Sustainability Campus Action (SCA) 2025 di tingkat fakultas. Kegiatan ini bertujuan memaparkan mekanisme pelaporan data keberlanjutan Fakultas Geografi yang akan dilaksanakan secara rutin setiap tahun hingga berakhirnya target SDGs pada 2030 mendatang.
Laboratorium Kewilayahan Departemen Geografi Pembangunan, Fakultas Geografi Universitas Gadjah Mada, melalui tim Praktikum Pengembangan Masyarakat Tahun 2025 (dosen pengampu Surani Hasanati, S.Si. M.Sc. bersama satu Asisten Departemen Dyah Pradjnya Paramitha, S.Si dan lima asisten praktikum Freya A. M. J. Putri, Anisa A. Fatmawati, S.Si., Fathoni Fathurrohman, Jesica E. D. Simangunsong, Intan J. C. Dewi, S.Si., serta 69 praktikan peserta mahasiswa), telah menyelenggarakan kegiatan akademik dengan praktik kepada masyarakat untuk membumikan Ilmu Geografi dan Pembangunan Wilayah pada sekolah jenjang pertama di Kota Yogyakarta.